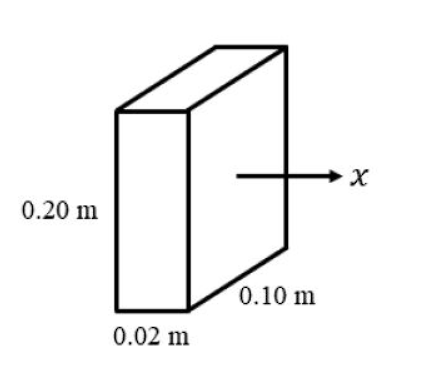
Consider the steady, uni-directional diffusion of a binary mixture of $A$ and $B$ across a vertical slab of dimensions $0.2 \mathrm{~m} \times 0.1 \mathrm{~m} \times 0.02 \mathrm{~m}$ as shown in the figure. The total molar concentration of $A$ and $B$ is constant at $100 \mathrm{~mol} \mathrm{~m}^{-3}$. The mole fraction of $A$ on the left and right faces of the slab are maintained at $0.8$ and $0.2$, respectively. If the binary diffusion coefficient $D_{A B}=1 \times 10^{-5} \mathrm{~m}^{2} \mathrm{~s}^{-1}$, the molar flow rate of $A$ in $\mathrm{mol} \mathrm{s}^{-1}$, along the horizontal $x$ direction is
- $6 \times 10^{-4}$
- $6 \times 10^{-6}$
- $3 \times 10^{-6}$
- $3 \times 10^{-4}$